DeFi offers a range of opportunities that aren’t available in traditional finance or even on centralized crypto exchanges.
You can earn higher interest rates on idle cash by lending stablecoins, often getting better rates than traditional savings accounts. DeFi platforms also give you access to invest in new and emerging tokens before they’re listed on major exchanges.
Additionally, you can borrow against your existing crypto assets without selling them and use leverage to enhance your borrowing power.
For all the above, DeFi platforms typically don’t require identity verification (KYC), so you can access financial services without sharing personal information, from almost anywhere in the world without sharing personal information.
Select and Install a DeFi Wallet
DeFi crypto wallets are digital wallets designed to interact with decentralized applications (dApps) on the blockchain. Unlike traditional crypto wallets, they’re built for the decentralized web and provide functionalities that go beyond just storing assets – you can actively use them within apps.
MetaMask browser extension download page. | Source: Metamask.io
Due to their frequent use, DeFi wallets often exist as browser extensions or mobile apps with their own built-in browsers. This allows them to be readily available for connecting to, and interacting with, dapps as needed.
In most cases, they’re completely non-custodial. This means that the funds remain in the user’s sole control at all times, and nobody. Nobody else has access to them.
These days, most of these wallets also support multiple blockchain networks, including assets built on those networks.
Some of the most popular DeFi wallets include:
- MetaMask Wallet: Most widely-used DeFi wallet.
- Coinbase Wallet: DeFi wallet developed by Coinbase exchange.
- Phantom: User-friendly wallet for Ethereum and Solana.
- Zerion: DeFi wallet with portfolio tracking.
- Trust Wallet: Official Binance DeFi wallet.
- Ledger: Most widely-integrated hardware wallet.
Fund Your DeFi Wallet With Crypto
Next, you’ll need some crypto in your DeFi wallet.
If you already own some crypto, simply locate your DeFi wallet’s public address and send tokens to it.
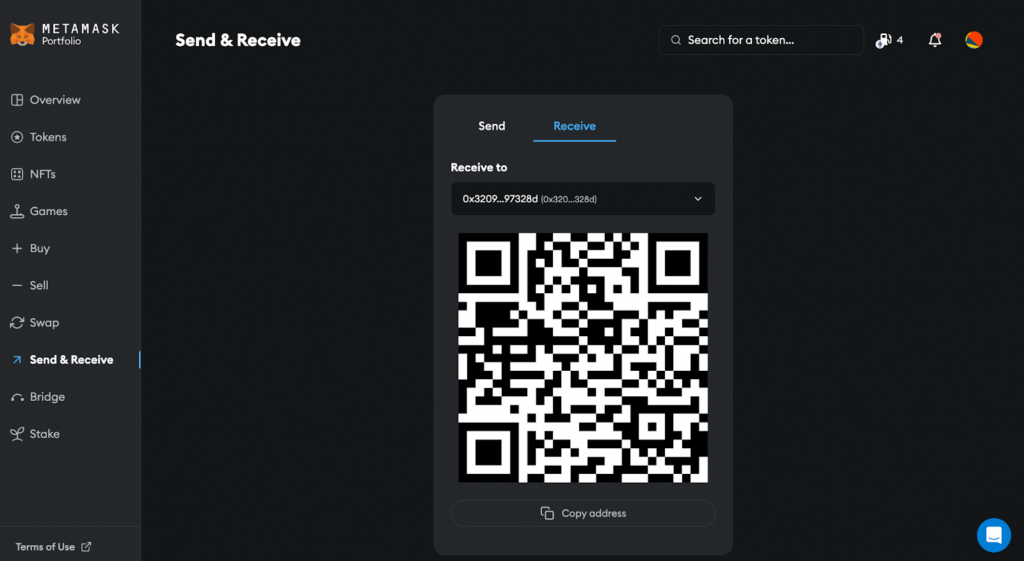
Public key (receiving address) in a DeFi wallet. | Source: Portfolio.metamask.io
If you need to buy some crypto, use the “buy” function in your DeFi wallet to buy instantly through one of the supported third party payments processors.
For larger amounts, it’s usually better to use a centralized exchange first and then withdraw the coins to your DeFi wallet. This option typically provides lower fees and larger purchase limits.
Note: You’ll want to make sure that at least a portion of your wallet balance is held in the network’s native token, in order to pay for transaction fees. If you’re using Ethereum, for example, you’ll want to hold part of your balance in ETH.
Choose and Use Decentralized Apps (DApp)
Now that you’re ready to go, you’ll want to find an app that suits your needs and preferences.
Here’s a brief overview of the different types of apps you can find in DeFi, along with some popular examples for each.
Connecting to the Uniswap app. | Source: App.uniswap.org
Lending & Borrowing Platforms
DeFi crypto lending and borrowing platforms let you lend your crypto to others to earn interest, just like earning interest in a savings account. You can also borrow money by using your crypto as collateral, which could be used as-is, or as leverage for more complex investment strategies.
Examples: Aave, Maker, Compound, Spark, Morpho.
Yield Aggregators
Yield aggregators automatically move your crypto between different DeFi protocols to get you the highest returns. Analyzing and optimizing various strategies ensuresBy analyzing and optimizing various strategies, they make sure your assets are always placed in the most profitable opportunities. This saves you time and effort, while maximizing your earnings.
Examples: YFI, Beefy, Convex Finance.
Decentralized Exchanges
A decentralized exchange (DEX) let’s you trade one type of token for another directly, using funds provided by other users to keep trades smooth. They don’t involve middlemen, making it a straightforward way to exchange assets.
Some DEXs also offer the trading of derivatives: complex financial products like futures and options contracts that allow you to use large degrees of leverage for larger trades.
Examples: Uniswap, Raydium, Curve, Pancakeswap, dYdX, Jupiter.
Liquid staking providers
Staking protocols let you lock up your crypto to earn rewards over time, like earning interest in a savings account. Liquid staking allows you to keep earning these rewards while also being able to trade your staked assets, giving you more flexibility.
Examples: Lido, Rocket Pool, Mantle LSP, Jito.
Predictions Markets
Prediction markets are platforms where people bet on the outcomes of future events, with the value of the bets reflecting the likelihood of those events happening.
They’re useful for capitalizing on predictions in areas like politics, finance, and sports, and can offer real-time updates based on collective opinions
Examples: Polymarket, Kalshi and Manifold.
Track and Manage Your Positions
In today’s DeFi landscape, assets can quickly become spread across different chains and DeFi protocols. This can make them hard to trackkeep track of in a normal DeFi wallet.
The solution to this is a portfolio asset management app.
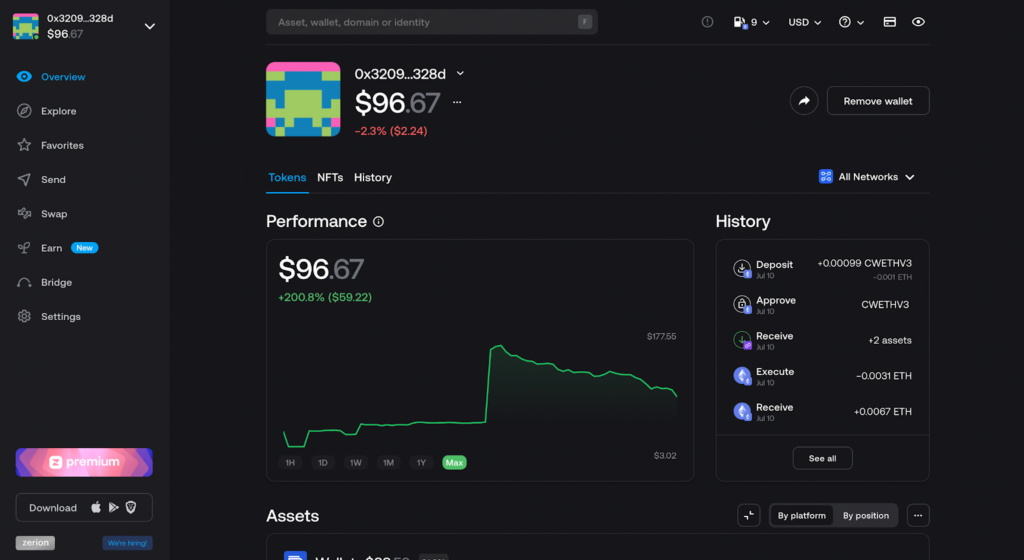
Zerion portfolio tracking dashboard. | Source: Zerion.io
Instead of searching through wallets and protocols, these platforms enable users to view and manage all of their positions within a single dashboard.
Some popular portfolio management apps include:
- Zapper: Social media-style DeFi asset management with token incentives.
- Zerion: Portfolio tracker and DeFi wallet in one.
- DeFi Saver: Advanced DeFi position and leverage management.
- Metamask Portfolio: Integrated MetaMask tracking with centralized exchange support.
- DeBank: Social DeFi platform with multichain support and paid messaging.
For a more detailed overview of DeFi portfolio apps, check out our page on DeFi portfolio management platforms.
Using Layer 2 Networks
Layer 2 networks are built on top of blockchains to enhance their speed, reduce transaction costs, and improve scalability.
These networks process transactions off the main blockchain for greater efficiency but still record network states on the main network to maintain security.
Many major projects have deployed their protocols on Layer 2 platforms, allowing users to take advantage of faster and cheaper transactions.
To use a Layer 2 network, follow these steps:
- Select a Layer 2: Choose a Layer 2 network that suits your needs.
- Add the Network to Your Wallet: Add support for that Layer 2 to your DeFi wallet, if it’s not already integrated.
- Bridge Funds: Transfer funds to the Layer 2 network using a bridge.
Make sure that the Layer 2 network supports both the DApps and the assets you wish to use – each Layer 2 is different.
Examples: Arbitrum, Base, Optimism, Polygon.
Understand DeFi Risks
Although DeFi eliminates gets rid of many human risks and errors, it’s still a new and developing space with its own new set of risks. Before investing any money you aren’t willing to lose, these should be fully understoodThese should be fully understood before investing any money you aren’t willing to lose.
One of DeFi’s biggest collapses. | Source: Bloomberg.com
Here are some DeFi-specific risks in more detail:
- Losing Private Keys: If you lose or fail to back up your private keys, your funds are likely gone forever. There’s no centralized organization that can recover them for you.
- Complexity and User Errors: DeFi platforms can be complex to use. Any mistakes in transactions or interacting with smart contracts can lead to the loss of funds.
- Smart Contract Bugs: DeFi platforms rely on smart contracts. Hackers could exploit any bugs or vulnerabilities in the code, causing funds to be lostAny bugs or vulnerabilities in the code could be exploited by hackers, leading to the loss of funds.
- Oracle Failures: DeFi platforms often rely on oracles to fetch off-chain data and price feeds. If an oracle fails or provides incorrect data, it can lead to smart contracts malfunctioning.
- Impermanent Loss: Providing liquidity to exchange pools can result in impermanent loss (IL). This is when the value of your assets ends up being lower compared to just holding them, due to market inefficiencies.
- Rug Pulls: Some DeFi projects can be scams, where developers withdraw and sell all their liquidity from a DEX. This is commonly known as a “rug pull.”
- Lack of Support: DeFi platforms require users to be more independent. Limited customer support for protocol or wallet issues can result in unresolved problems.
You can minimize these risks by sticking to trusted and well-audited DeFi apps, doing due diligence, securely storing your private keys, and maintaining good risk management with your asset allocations.
Conclusion
DeFi opens up a world of financial opportunities not available in traditional finance. It allowsthat aren’t available in traditional finance, allowing you to earn interest, invest in new tokens, and borrow against your assets with ease.
By choosing the right tools and practicing good risk management, you’ll be well on your way to navigating the DeFi space safely and fully utilizing taking full advantage of its benefits.

