The DeFi ecosystem started with Ethereum but has since rapidly expanded to include a growing number of different blockchain networks.
As this happens, there’s an increasing need for these blockchains to be able to “talk” to each other and share assets.
DeFi bridges are one of the key tools for this.
While regular DEXs are used to swap between assets within a single chain, bridges are platforms that let users move assets from one blockchain to another.
Best DeFi Bridges for DEX Trades: Cross Chain Swaps
Here’s a look at some top DeFi bridges, how they work, and what makes them stand out – from fast transfers to past challenges like hacks.
| Protocol Name | Chains Supported | Type of Bridge | Fees | Hacks | Unique Features |
| Stargate (LayerZero) | 40+ | Lock-and-mint + Liquidity pools | 0.06%, pool rebalance fees | No major hacks | Fast one-click transfers, Oracle/Relayer verification |
| Portal (Wormhole) | 30+ | Lock-and-mint | 0.05%–0.2% | $326M (Feb 2022) | NFT support, gasless bridging |
| Across Protocol | 6+ EVM | Liquidity pools (intent-based) | 0.05%–0.15% | No major hacks | Intent-based, UMA oracle, fast settlement (<1 min) |
| THORSwap (THORChain) | 17+ (non-EVM) | Liquidity pools (native swaps) | 0.5% | $7.6M (2021), $200M debt (2025) | Native swaps, 6,000+ assets, staking/yield |
| Jumper (LI.FI) | 25+ | Aggregator | Route-dependent | No direct hacks, inherited risks | One-click swaps |
| Bungee (Socket) | 10+ (EVM) | Aggregator | Route-dependent; Refuel fee | $3.3M (Jan 2024) | Refuel gas top-up |
1. Stargate (LayerZero)
Stargate is a bridge built on a technology called LayerZero, which makes it super quick and easy to move tokens like USDC or ETH between blockchains.
Instead of slow, risky bridges with several steps, it lets you send tokens in one click across 40+ blockchains using shared liquidity pools.
LayerZero checks transactions by having two helpers (an Oracle and a Relayer) confirm messages through a simple system on each blockchain.
LayerZero itself has raised more than $260 million, from investors including a16z and Sequoia.
| Chains Supported | 40+ |
| Type of Bridge | Lock-and-mint + liquidity pools |
| Fees | 0.06% transaction fee, pool rebalance fees for large transactions |
| Hacks | No major hacks. LayerZero patched some vulnerabilities in 2022 |
| Funding & Team | LayerZero Labs: $263.3M raised from a16z, Sequoia, and othersLed by Bryan Pellegrino and Ryan Zarick |
2. Portal (Wormhole)
Portal is an app built on Wormhole protocol that makes moving tokens and NFTs between blockchains simple.
It locks your asset on one chain, like Ethereum, and mints a wrapped version on another, like Solana, in seconds.
It has a sleek interface and supports over 30 chains. It also offers features like native-to-native swaps and gasless bridging, letting you swap without the need for native tokens on the other side.
Wormhole is a protocol that connects different blockchains, using a network of 19 validators called “Guardians” to verify transactions.
In February 2022, hackers stole $320 million from Wormhole’s core system by exploiting a flaw in its Solana-Ethereum bridge (not the Portal Bridge app itself). Jump Crypto, the crypto division of Jump Trading, quickly replaced the stolen ETH to keep Wormhole running and protect users.
| Chains Supported | 30+ |
| Type of Bridge | Lock-and-mint |
| Fees | 0.05% to 0.2% |
| Hacks | $326M exploit in Feb 2022. Jump Crypto bailed out users. |
| Funding & Team | Wormhole: $225M raised Run by ex-Jump Trading engineers, 19 validators |
3. Across Protocol

Across Protocol is a cross-chain bridge that lets you move tokens between EVM blockchains, like Ethereum and Layer 2s.
Its system uses “intents,” where you state what you want (e.g. to swap X for Y), and then relayers compete to fill those orders fast.
Relayers get paid only after an oracle confirms the transfer is legit, through a process where anyone can challenge mistakes.
It’s protected by UMA’s optimistic oracle – a verification tool that checks transfers, and makes sure they’re safe and efficient.
| Chains Supported | 6+ EVM chains |
| Type of Bridge | Liquidity pools (intent-based) |
| Fees | 0.05% to 0.15% (relayer fees) |
| Hacks | No major hacks reported |
| Funding & Team | Risk Labs (Across and UMA developer): $7.9M raised from Coinbase Ventures, Blockchain Capital, and others. Team led by Hart Lambur |
4. THORSwap (THORChain)
THORSwap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) that lets you trade native crypto assets, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, across different blockchains using THORChain’s liquidity network.
It connects liquidity pools to swap tokens directly, offering low fees and protection against impermanent loss.
With a user-friendly interface, it supports over 6,000 assets across 17+ chains, letting you trade, stake, or earn yield without custodians.
It’s like a one-stop shop for cross-chain DeFi, powered by the $THOR token for governance and rewards.”
ThorChain itself is secured by node operators that bond the platform’s native RUNE token. This makes sure that funds stay safe and user-controlled.
| Chains Supported | 17+ (Focus on non-EVM chains) |
| Type of Bridge | Liquidity pools (native swaps) |
| Fees | 0.5% |
| Hacks | $7.6M exploit of THORChain in 2021, users were reimbursed.THORChain paused operations to fix $200M debt in Jan 2025. |
| Funding & Team | No venture funding. Nodes incentivized via $RUNE Pseudonymous team, project community-driven. |
5. Multichain (Now Defunct)

Multichain, which is no longer operational, was a cross-chain bridge that let users transfer tokens and data between 90+ blockchains.
It used a network of nodes to lock assets on one chain and mint equivalents on another, aiming for fast and flexible transfers.
The protocol supported one of the biggest ranges of chains and was popular for DeFi, but relied on a very centralized MPC (multi-party computation) system for security.
Because of this setup, Multichain collapsed in 2023.
In May 2023, Chinese authorities arrested CEO Zhaojun He , who solely controlled the multi-party computation (MPC) servers that processed transfers. This locked the team out of critical systems hosted on his personal cloud account.
A $125 million hack on July 6 exploited compromised MPC keys, possibly an inside job, draining user funds.
With no server access, Zhaojun’s sister moved $220 million to new wallets before her arrest on July 13, and Multichain shut down on July 14 – unable to operate or recover.
| Chains Supported | 90+ |
| Type of Bridge | Lock-and-mint |
| Fees | 0.05% to 0.25% |
| Hacks | $200M exploit in July 2023, led to shutdown |
| Funding & Team | $60M raised in 2021-2022 Led by Zhaojun He (arrested in 2023) |
What is a DeFi Bridge?
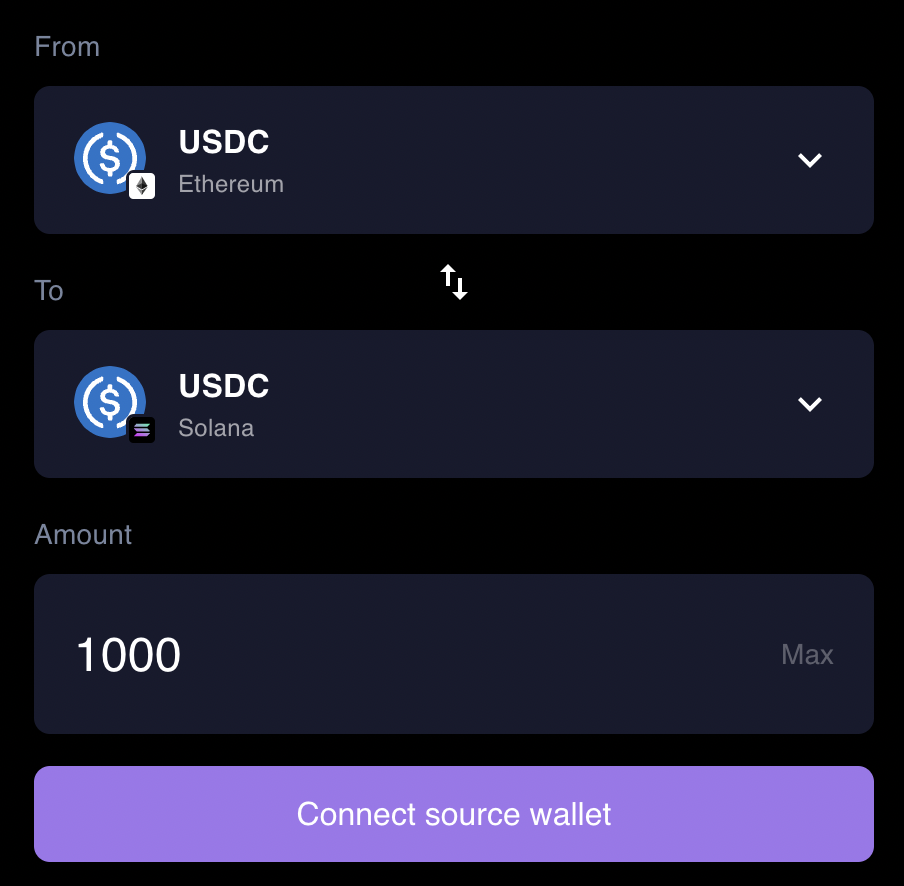
A DeFi bridge is any tool that can send funds from one blockchain to another, without the need for a middleman.
For example, imagine that I have USDC on Ethereum, and I see that lending USDC on Solana provides a better interest rate. I’d like to move it over to take advantage of that improved rate.
The problem is, those two networks exist separately – and they’re not compatible with each other.
Without DeFi bridges, I‘d have to try to trade my Ethereum USDC off-chain with someone willing to give up their Solana-based USDC.
Or even worse, I’d have to sell it for dollars, then those dollars to buy USDC on Solana afterward.
Each of those two options requires a trust-based setup. This means counting on a person or a centralized exchange to facilitate the trade faithfully, rather than letting computer code do the job (as you would with smart contracts).
A DeFi bridge solves this problem. It keeps things on-chain, so that you can trustlessly swap your assets from one chain to another – with no middleman involved.
Why DeFi Bridges Matter
DeFi bridges are the glue holding the multi-chain DeFi ecosystem together. Here’s why they’re useful:
- Interoperability: They connect blockchains like Ethereum (EVM) and Solana (non-EVM), letting you use protocols across ecosystems – even if they aren’t directly compatible.
- Improved Liquidity: Some bridges link liquidity pools together, making large transfers or swaps possible with minimal slippage.
- New Use Cases: Bridges enable cross-chain lending (deposit on Ethereum, borrow on Arbitrum) or omnichain NFTs (buy on Ethereum with AVAX). Radiant Capital’s omnichain money markets are a prime example.
If you’re still unsure, we have a page that explains how a DEX works.
Best DeFi Bridge Aggregators
Cross-chain bridge aggregators are platforms that simplify moving or swapping crypto assets across blockchains by finding the best route through multiple bridges and DEXs in one click. They save users time and money by comparing fees, speed, and liquidity, acting like a crypto travel agent for seamless DeFi transfers.
1. Jumper

Jumper Exchange is a cross-chain aggregator built on the LI.FI protocol, supporting 25+ blockchains by combining multiple bridges and DEXs for seamless token transfers and swaps.
The platform makes moving tokens like USDC or ETH between blockchains super simple by finding the best path through bridges like Stargate or Wormhole and DEXs like Uniswap.
You pick your tokens and chains, and Jumper handles the transfer or swap in one click, saving you time and money.
| Chains Supported | 25+ |
| Type of Bridge | Aggregator |
| Fees | Depends on route |
| Hacks | No direct hacks; inherits risks from bridges (e.g., Wormhole’s 2022 exploit) |
| Funding & Team | LI.FI: $23.5M raised (Series A 2022, $17.5M; 1kx, Dragonfly); team led by Philipp Zentner, ex-1inch contributor |
2. Bungee (Socket Protocol)
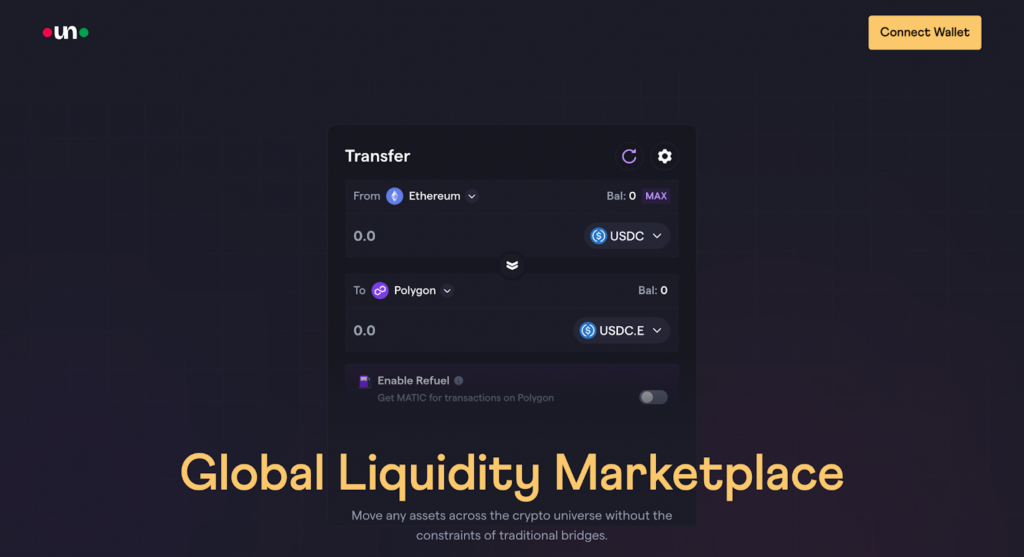
Bungee Exchange is a cross-chain aggregator that’s built using Socket Protocol. It supports 10+ blockchains with a focus on user-friendly transfers and a unique Refuel feature for gas top-ups.
It lets you move tokens like MATIC or ETH across blockchains easily by picking the best route through bridges like Hop or Stargate and DEXs like 1inch.
With a simple interface, it does the transfer or swap in one step and can even send a bit of gas (like ETH) to the new chain so you’re ready to go.
It shows all fees clearly, and it’s perfect for beginners who want a smooth DeFi experience across chains.
| Chains Supported | 10+ (EVM focused) |
| Type of Bridge | Aggregator |
| Fees | Depends on route. Refuel adds a small gas fee. |
| Hacks | $3.3M hack in January 2024, from a Socket Protocol “infinite approvals” bug. |
| Funding & Team | Socket: $8M raised from Coinbase Ventures and Framework Ventures Pseudonymous team |
How DeFi Bridges Work
There are various ways that DeFi bridges can work, using different systems to achieve cross-chain compatibility.
Here’s a breakdown of the three main systems you’ll see under the hood of the top DeFi bridges:
- Lock + Mint: Tokens are locked in a smart contract on the source chain (e.g. Ethereum), and a “wrapped” version is minted on the destination chain (e.g. Solana). This wrapped version of the token is redeemable later for the original.
- Burn + Release: Tokens are burned on the source chain, and an equivalent amount is released on the destination chain. This keeps the supply of those tokens consistent.
- Liquidity-Based Systems: These bridges use shared liquidity pools across chains, enabling direct transfers or swaps without wrapping, for a smoother experience.
As you can imagine, each method has its own trade-offs.
Lock-and-mint is simple, but creates wrapped assets instead of native ones. Burn-and-release makes sure you get native tokens on both ends, but needs tight security. Liquidity pools need deep reserves to avoid slippage.
Degrees of Decentralization
There’s also a difference in how bridges are powered and how decentralized they are.
They can either depend on smart contracts entirely, or partially rely on a handful of parties called “validators”.
Validator-based systems depend on a handful of trusted parties (like blockchain bank tellers) who check and approve transfers.
Completely trustless systems use smart contracts and cryptographic proofs (like zero-knowledge) to verify transactions, minimizing reliance on anyone in between.
In general, the more secure, the slower a bridge is – so it’s up to the developers to find a functional middleground.
Risks & Challenges
As a new and developing technology, DeFi bridges obviously have their fair share of risks and challenges.
Here are some of the shortfalls you’ll want to know about before using a DeFi bridge:
Hacks and smart contract risks
Like any platform that handles money, DeFi bridges become targets for hackers. This often involves exploiting buggy code in smart contracts.
As you might have noticed in the platform summaries above, this has already resulted in the loss of hundreds of millions of dollars in funds.
Whether it’s coding errors in the bridge’s software, too much control in one team member’s hands, or weak security in the systems (like validators or oracles) – if there’s a gap, it will eventually be exploited.
UX friction and transaction delays
A more minor issue that’s associated with DeFi bridges is the clunky user experience.
This is naturally an issue, due to the complexity of what’s going on behind the scenes. It’s also a tough one to fix, especially if you want to maintain a high level of security.
The problem is that cross-chain transfers deal with multiple blockchain networks, several transaction steps, and multiple wallets.
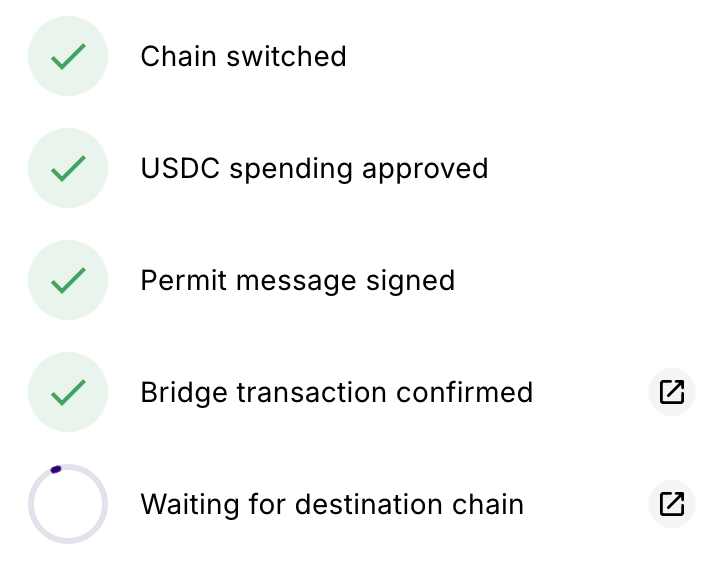
That means switching between networks, approving token approvals, and approving a lot of transactions – turning what should be an easy experience into a multi-step process.
Fragmented liquidity across chains
Fragmented liquidity means that crypto tokens, like USDC, are split across different blockchains.
Each chain has its own separate stash of funds, which creates problems for DeFi bridges. This setup makes trading less efficient, because small pools on each chain lead to worse prices and higher slippage.
For large transactions, it can also drive up costs and slow down transfers. The limited funds on the other side can make moving tokens between chains expensive and risky.
The tradeoff between speed and security
Everyone wants faster results – but nobody wants their funds stolen.
Unfortunately, the tradeoff between speed and security in DeFi bridges means that faster token transfers often come at the cost of weaker protection, creating a tough balance for users.
Some bridges prioritize speed by using quick verification systems, like oracles or relayers, to move tokens in seconds. At the same time, these can be vulnerable to hacks if they’re not tightly secured.
Slower bridges, like those with multi-step validator checks or longer confirmation times, are often safer because they allow more time to catch errors or fraud. On the other hand, they frustrate users who want instant results.
The Future of DeFi Bridges
Moving toward native cross-chain DeFi
DeFi is already developing more of a cross-chain focus at the app level, trying to build-in this capability behind the scenes.
The target is to let you feel like you’re using one chain, even if you’re not.
UniswapX is a great example of this shift.
Instead of acting like a traditional bridge, it uses third-party fillers to handle routing and bridging behind the scenes, using existing infrastructure.
Users just make a swap request, and the system figures out the best way to complete it, even across multiple chains.
This kind of design reduces friction, boosts security, and helps DeFi move toward a more connected, user-friendly experience.
Instead of scaring off users, the tech just works for them in the background.
Increasing demand for seamless UX
The overall DeFi user experience continues to be a key hurdle for mass adoption.
Developments like abstraction are a step in the right direction for providing a more seamless experience that doesn’t feel daunting like the current state of affairs.
Abstraction is the process of tucking away the complexities of DeFi behind the scenes, to let users transact in a more intuitive way. This means less confirming transactions and less switching networks while the heavy lifting is done in the background.
Some perks abstraction has enabled so far includes:
- Logins with familiar credentials instead of seed phrases
- Skipping complex wallet setups
- Removes the need to hold native gas tokens
- Offers one-click interfaces.
Potential regulatory implications
As crypto becomes more closely regulated, DeFi bridges face potential pressure that could slow them down or raise costs.
Governments worry about unregulated transfers, especially with semi-centralized bridges like Multichain, which shut down after its CEO was arrested in China.
New rules may require ID checks, licenses, and stablecoin restrictions – particularly in places like the EU under Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA).
In the US, there’s no unified law, so bridges deal with a patchwork of agency and state rules. But with situations like the US Treasury’s sanctioning of the Tornado Cash contract address (now retracted),
Fully decentralized bridges are mostly safe for now, but others might need to adapt to stay compliant.

